Selecting the right polishing head can make or break your finishing project. Whether you're working on metal fabrication, woodworking, or automotive restoration, the polishing head you choose directly impacts surface quality, work efficiency, and overall project success. Modern manufacturing demands have evolved significantly, requiring more specialized approaches to surface finishing that deliver consistent, professional results across diverse applications.
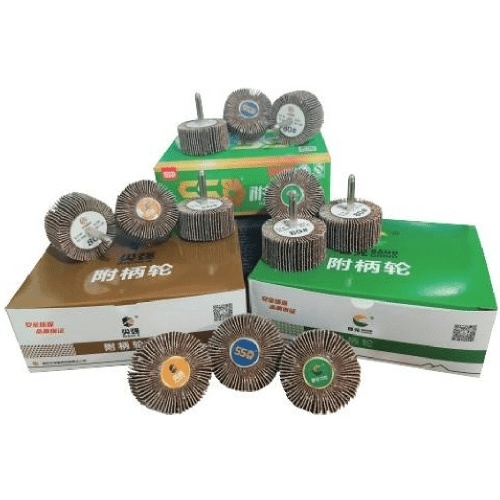

Industry professionals understand that surface preparation and finishing operations require careful consideration of material compatibility, grit progression, and application-specific requirements. The complexity of today's manufacturing processes means that choosing an inadequate polishing solution can result in costly rework, extended project timelines, and compromised quality standards. This comprehensive guide addresses the critical factors that influence polishing head selection for professional applications.
Understanding Polishing Head Fundamentals
Core Construction and Design Principles
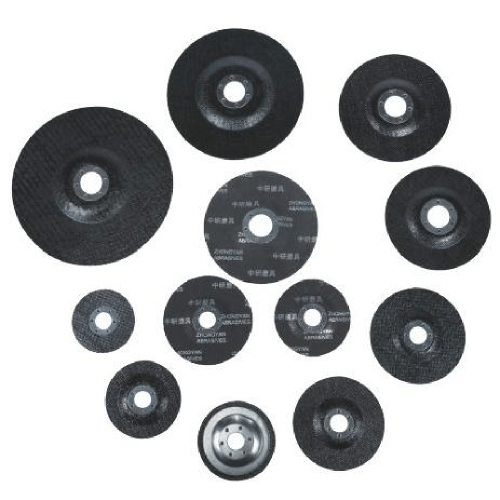
The foundation of any effective polishing head lies in its construction methodology and material composition. High-quality units feature precision-engineered backing systems that provide consistent pressure distribution across the working surface. The backing material must withstand rotational forces while maintaining dimensional stability under varying temperature conditions. Professional-grade options incorporate advanced bonding agents that secure abrasive materials without compromising flexibility during operation.
Modern polishing head designs integrate multiple engineering considerations including heat dissipation, debris removal, and operator safety features. The geometric configuration affects cutting action, surface contact patterns, and material removal rates. Manufacturers employ sophisticated testing protocols to validate performance characteristics across different operational parameters, ensuring reliable results in production environments.
Material Selection and Performance Characteristics
Abrasive material selection significantly influences polishing effectiveness and longevity. Aluminum oxide variants offer excellent versatility for general-purpose applications, providing consistent cutting action across diverse substrates. Silicon carbide formulations excel in specific applications requiring aggressive material removal or specialized surface textures. Ceramic abrasives deliver superior performance in high-temperature applications while maintaining sharp cutting edges throughout extended use cycles.
The grain size distribution within each polishing head determines surface finish characteristics and material removal rates. Coarser grits enable rapid stock removal during initial preparation stages, while finer formulations produce mirror-like finishes for critical applications. Understanding grit progression principles helps optimize workflow efficiency and achieve specified surface quality requirements.
Application-Specific Selection Criteria
Metal Finishing Applications
Metal polishing applications demand specialized consideration of substrate hardness, surface contamination, and desired finish quality. Ferrous metals typically respond well to aluminum oxide formulations that provide consistent cutting action without excessive heat generation. Non-ferrous materials such as aluminum, brass, and copper require different approaches to prevent material buildup and maintain optimal cutting performance.
Stainless steel finishing presents unique challenges due to work hardening characteristics and heat sensitivity. Selecting the appropriate polishing head involves balancing cutting efficiency with heat management to prevent surface damage or discoloration. Professional applications often require multiple grit progressions to achieve specified surface roughness values while maintaining dimensional accuracy.
Woodworking and Composite Materials
Wood finishing applications benefit from polishing head designs that accommodate grain structure variations and minimize surface tearing. Open-grain hardwoods require different approaches compared to dense, fine-grain species. The polishing head selection must account for wood density, moisture content, and intended finish application to achieve optimal results.
Composite materials including engineered wood products, laminates, and fiber-reinforced plastics present distinct challenges for surface preparation. These materials often combine multiple substrate types within a single component, requiring polishing heads that adapt to varying material properties without compromising surface integrity. Temperature management becomes critical when working with thermoplastic components that may deform under excessive heat generation.
Performance Optimization Strategies
Speed and Pressure Considerations
Operational parameters significantly influence polishing head performance and service life. Rotational speed affects material removal rates, surface finish quality, and heat generation. Higher speeds generally increase productivity but may compromise surface quality in sensitive applications. Finding the optimal balance requires understanding material properties, polishing head characteristics, and specific application requirements.
Applied pressure during polishing operations directly impacts cutting efficiency and tool wear patterns. Excessive pressure can lead to premature polishing head failure, surface damage, or safety hazards. Insufficient pressure results in poor material removal rates and extended processing times. Professional operators develop technique through experience and training to maintain consistent pressure application throughout the operation.
Heat Management and Cooling Strategies
Heat generation during polishing operations affects both workpiece quality and polishing head longevity. Excessive temperatures can cause material property changes, surface discoloration, or thermal damage to temperature-sensitive substrates. Effective heat management strategies include proper speed selection, adequate cooling provision, and appropriate contact pressure maintenance.
Some applications benefit from wet polishing techniques that provide continuous cooling and debris removal. Water-based coolants help maintain consistent temperatures while extending polishing head service life. However, wet operations require additional considerations including corrosion prevention, waste disposal, and workplace safety measures to prevent slip hazards.
Quality Assessment and Selection Guidelines
Performance Testing Methods
Evaluating polishing head quality requires systematic testing approaches that measure relevant performance characteristics. Surface finish measurement using profilometry or visual inspection standards provides objective quality assessment. Material removal rate testing determines productivity potential under controlled conditions. Durability testing evaluates service life expectations and wear patterns under typical operating conditions.
Comparative testing between different polishing head options helps identify the most suitable choice for specific applications. Testing protocols should replicate actual working conditions including material types, operational parameters, and environmental factors. Documentation of test results enables informed decision-making and establishes baseline performance expectations for production applications.
Cost-Benefit Analysis Framework
Total cost of ownership extends beyond initial purchase price to include operational efficiency, service life, and quality consistency factors. Higher-quality polishing head options may justify premium pricing through extended service life, improved productivity, or superior finish quality. Economic analysis should consider labor costs, material waste, rework expenses, and downtime implications when comparing alternatives.
Production volume considerations influence polishing head selection priorities. High-volume operations benefit from durable, consistent-performing options that minimize changeover frequency and maintain quality standards. Lower-volume or specialty applications may prioritize versatility and specific performance characteristics over extended service life requirements.
Maintenance and Storage Best Practices
Proper Handling Techniques
Polishing head longevity depends significantly on proper handling and storage practices. Avoiding impact damage during installation and removal prevents premature failure and maintains dimensional accuracy. Clean storage environments protect abrasive surfaces from contamination that could affect cutting performance or cause surface defects during subsequent use.
Regular inspection routines help identify wear patterns, damage, or contamination before they impact work quality. Visual examination of abrasive surfaces, backing integrity, and mounting hardware ensures safe operation and optimal performance. Establishing inspection schedules based on usage patterns helps optimize replacement timing and prevent unexpected failures during critical operations.
Environmental Storage Considerations
Environmental conditions during storage affect polishing head performance and service life. Humidity control prevents moisture absorption that could weaken bonding agents or cause dimensional changes. Temperature stability prevents thermal cycling that might compromise structural integrity or abrasive adhesion. Proper packaging protects against physical damage and contamination during storage periods.
Inventory rotation practices ensure that older stock receives priority use before degradation affects performance. Dating systems and first-in-first-out protocols help maintain consistent quality standards while minimizing waste from expired or deteriorated products. Climate-controlled storage facilities provide optimal conditions for long-term inventory management in professional operations.
FAQ
What factors determine the optimal grit size for my polishing application
Grit size selection depends on material hardness, initial surface condition, and desired finish quality. Coarser grits (40-120) handle heavy material removal and rough surfaces, while finer grits (220-400+) produce smooth finishes. Consider the complete grit progression needed to transition from initial preparation to final finishing requirements efficiently.
How do I prevent overheating during extended polishing operations
Heat management requires balancing operational speed, contact pressure, and cooling provisions. Reduce rotational speed or applied pressure if excessive heat develops. Consider wet polishing techniques for heat-sensitive materials. Allow periodic cooling intervals during extended operations and ensure adequate ventilation around the work area to dissipate generated heat effectively.
What safety precautions should I observe when using polishing heads
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment including safety glasses, dust masks, and hearing protection. Inspect polishing heads for damage before use and ensure proper mounting on compatible equipment. Maintain recommended speed limits and avoid excessive pressure application. Keep loose clothing and long hair away from rotating equipment and maintain clean work areas to prevent slip hazards.
How can I extend the service life of my polishing heads
Proper operational techniques significantly impact polishing head longevity. Use appropriate speeds and pressures for your specific application. Keep the polishing head clean and free from debris buildup. Store in controlled environmental conditions and handle carefully to prevent damage. Rotate usage among multiple units to allow cooling between operations and maintain consistent performance standards throughout the service life.