When it comes to metalworking and surface preparation tasks, professionals often find themselves choosing between two essential abrasive tools. Understanding the fundamental differences between these grinding accessories can significantly impact your project outcomes, efficiency, and overall cost-effectiveness. Both options serve specific purposes in industrial applications, yet their unique characteristics make them suitable for different scenarios and material requirements.

The selection process involves evaluating multiple factors including material compatibility, surface finish requirements, tool longevity, and operational safety considerations. Professional fabricators and maintenance technicians must carefully assess their specific application needs to determine which abrasive solution delivers optimal performance. This comprehensive analysis will explore the technical specifications, practical applications, and performance characteristics of both grinding solutions to help you make informed decisions for your workshop or industrial facility.
Understanding Abrasive Tool Fundamentals
Construction and Design Principles
Traditional grinding wheels feature a solid construction with abrasive particles bonded throughout the entire wheel structure using resin, vitrified, or rubber bonding agents. This uniform distribution creates a consistent cutting surface that maintains its shape throughout the grinding process. The wheel's rigidity provides excellent dimensional stability and precise material removal capabilities, making it ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances and consistent results.
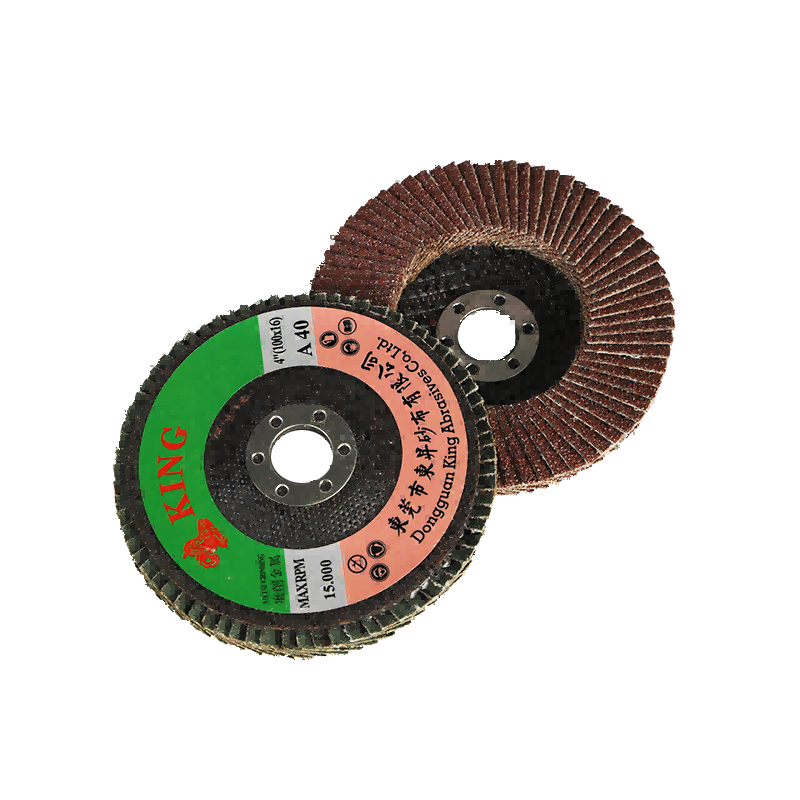
In contrast, a flap disc incorporates overlapping abrasive cloth flaps arranged around a central backing plate in a radial pattern. This flexible construction allows the individual flaps to conform to surface contours while providing a cushioned grinding action. The overlapping design ensures continuous fresh abrasive exposure as outer layers wear away, delivering consistent performance throughout the disc's operational life.
Material Composition Variations
Grinding wheels typically utilize aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, or ceramic abrasive grains depending on the intended application and target material. The grain size distribution and bonding agent selection directly influence cutting characteristics, wheel hardness, and thermal properties. Harder bonds provide longer wheel life but generate more heat, while softer bonds offer cooler cutting action with faster wheel consumption rates.
Flap disc abrasive cloths commonly feature aluminum oxide, zirconia alumina, or ceramic grain materials backed by polyester or cotton cloth substrates. The cloth backing provides flexibility and tear resistance while the abrasive coating delivers consistent material removal rates. Advanced grain treatments and cooling additives enhance performance on heat-sensitive materials and extend operational life in demanding applications.
Performance Characteristics and Capabilities
Material Removal Rates and Efficiency
Grinding wheels excel in heavy material removal applications where aggressive cutting action and high stock removal rates are required. The rigid wheel structure maintains consistent geometry under load, enabling deeper cuts and faster material removal on thick sections. Professional metalworkers rely on grinding wheels for roughing operations, weld preparation, and heavy-duty surface conditioning tasks where maximum productivity is essential.
Flap disc performance emphasizes controlled material removal with superior surface finish quality. The flexible flap construction provides a self-sharpening action that continuously exposes fresh abrasive particles while cushioning the cutting action to reduce gouging and surface damage. This characteristic makes flap disc tools particularly effective for finish grinding, blending operations, and applications requiring smooth surface transitions without deep scratches or grinding marks.
Heat Generation and Thermal Management
Heat buildup during grinding operations can significantly impact workpiece metallurgy, tool life, and operator safety. Grinding wheels generate substantial heat due to their aggressive cutting action and solid construction, particularly when used with improper technique or excessive pressure. Adequate coolant flow and proper grinding parameters become critical for maintaining workpiece integrity and preventing thermal damage to heat-treated materials.
The flexible nature of flap disc construction promotes better heat dissipation through improved air circulation around individual flaps. This design reduces heat concentration at the grinding interface while the cloth backing provides additional thermal insulation. Lower operating temperatures extend tool life, reduce workpiece distortion, and improve operator comfort during extended grinding sessions.
Application-Specific Advantages
Precision Grinding and Dimensional Control
Manufacturing environments requiring precise dimensional control and consistent surface geometry typically favor grinding wheel applications. Tool and die shops, precision machining facilities, and aerospace manufacturers rely on grinding wheels for their ability to maintain exact profiles and deliver repeatable results. The rigid wheel structure resists deflection under load, enabling accurate material removal within tight tolerances.
Surface preparation tasks often benefit from flap disc flexibility and conformability characteristics. Curved surfaces, irregular geometries, and contoured workpieces present challenges that grinding wheels cannot effectively address due to their inflexible nature. Flap disc tools adapt to surface variations while maintaining consistent contact pressure, resulting in uniform surface preparation across complex geometries.
Versatility in Material Applications
Different materials respond uniquely to various grinding approaches based on their hardness, thermal sensitivity, and structural characteristics. Grinding wheels perform exceptionally well on ferrous metals, cast iron, and hardened steel components where aggressive material removal is necessary. The wheel's ability to maintain sharp cutting edges through proper dressing procedures ensures consistent performance across diverse metalworking applications.
Aluminum, stainless steel, and other non-ferrous materials often load grinding wheels due to their tendency to smear and clog abrasive surfaces. Flap disc construction naturally resists loading through continuous self-cleaning action as individual flaps flex and shed accumulated debris. This characteristic makes flap disc tools particularly effective for soft metals, painted surfaces, and materials prone to clogging traditional abrasive wheels.
Economic Considerations and Cost Analysis
Initial Investment and Tool Costs
Budget considerations play a crucial role in abrasive tool selection for both individual craftsmen and large manufacturing operations. Grinding wheels typically offer lower initial purchase costs, especially for basic aluminum oxide formulations used in general metalworking applications. Volume purchasing agreements and standardized sizing make grinding wheels an economical choice for high-volume production environments with predictable consumption patterns.
Flap disc pricing reflects the more complex manufacturing process required to produce and assemble individual abrasive flaps onto backing plates. Premium grain formulations and advanced cloth substrates further increase material costs compared to conventional grinding wheels. However, the extended operational life and reduced changeout frequency often offset higher initial investment through improved productivity and reduced downtime.
Long-term Operational Costs
Total cost of ownership encompasses tool consumption, labor efficiency, and secondary operations required to achieve desired surface finish quality. Grinding wheels may require frequent dressing operations to maintain cutting efficiency and geometric accuracy, adding both time and material costs to grinding operations. Wheel breakage and premature wear in challenging applications can significantly impact operational budgets.
The self-sharpening nature of flap disc construction eliminates dressing requirements while providing consistent performance throughout the tool's operational life. Reduced grinding time per workpiece and elimination of secondary finishing operations often result in lower total processing costs despite higher initial tool investment. Improved surface quality may eliminate downstream polishing or finishing steps, further enhancing overall economic benefits.
Safety Considerations and Best Practices
Operational Hazards and Risk Management
Grinding wheel operations present significant safety risks including wheel burst potential, operator injury from flying debris, and exposure to harmful dust particles. Proper wheel mounting, speed verification, and regular inspection procedures are essential for safe operation. Ring testing before installation helps identify potential defects that could lead to catastrophic failure during use.
Flap disc construction inherently provides improved safety characteristics through its flexible design that resists catastrophic failure modes. Individual flap separation represents a gradual wear process rather than sudden wheel disintegration, reducing injury risks from flying debris. The cushioned grinding action also reduces kickback potential and provides better operator control during handheld applications.
Personal Protective Equipment Requirements
Both grinding methods require comprehensive personal protective equipment including safety glasses, face shields, hearing protection, and respiratory equipment appropriate for the materials being processed. Grinding wheel operations typically generate more aggressive debris and require higher levels of eye and face protection due to increased particle velocity and size.
Dust collection systems become particularly important when processing materials that generate harmful airborne particles such as stainless steel, aluminum, or painted surfaces. Flap disc grinding typically produces finer dust particles that may require enhanced filtration systems compared to the coarser debris generated by conventional grinding wheels.
Selection Criteria for Optimal Performance
Workpiece Material Compatibility
Material hardness, thermal sensitivity, and surface finish requirements serve as primary factors in determining optimal abrasive tool selection. Hard steels, cast iron, and carbide materials typically respond well to aggressive grinding wheel action, while softer materials may benefit from the controlled cutting action provided by flap disc construction.
Specialized applications such as stainless steel fabrication, aluminum processing, or exotic alloy machining may require specific grain formulations and backing materials optimized for particular material characteristics. Understanding metallurgical properties and thermal limitations helps ensure appropriate tool selection for critical applications.
Surface Finish Requirements
Final surface quality expectations significantly influence tool selection decisions across various industries. Applications requiring mirror finishes or specific surface roughness values may necessitate multiple grinding steps with progressively finer abrasive grades. Grinding wheels excel in roughing operations but may require extensive finishing work to achieve smooth surface textures.
Flap disc tools often eliminate the need for multiple grinding steps by providing controlled material removal with superior surface finish quality in a single operation. The graduated wear pattern creates progressively finer cutting action as the tool ages, naturally improving surface finish throughout the grinding process.
FAQ
What determines the lifespan difference between grinding wheels and flap discs
Tool lifespan depends on several factors including material hardness, application pressure, and grinding technique. Grinding wheels typically provide consistent performance until worn completely, while flap discs offer extended operational life through continuous fresh abrasive exposure. Proper technique and appropriate tool selection for specific applications maximize both tool types' operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Can both tools be used interchangeably on the same grinder
Most angle grinders and portable grinding equipment accommodate both wheel types using standard mounting systems, though specific size and thread compatibility should be verified. Operational speeds and safety requirements may differ between tool types, requiring operator training and equipment adjustments. Always verify manufacturer specifications and safety guidelines before switching between different abrasive tool types.
Which option provides better value for occasional DIY use
Occasional users often benefit from flap disc versatility and extended storage life compared to grinding wheels that may deteriorate over time. The forgiving nature of flap disc construction reduces learning curve requirements while providing consistent results across various projects. However, specific applications and budget constraints should guide final selection decisions based on individual project requirements.
How do environmental factors affect tool performance
Humidity, temperature, and storage conditions significantly impact both tool types through different mechanisms. Grinding wheels may absorb moisture and lose structural integrity, while flap discs can experience cloth backing degradation in extreme conditions. Proper storage in controlled environments and regular inspection protocols help maintain optimal tool performance regardless of environmental challenges.